Everyone should have an SEO audit done for their website on a regular basis, just as everyone should have car maintenance done or an annual physical. An SEO audit tells you the health of your website with regards to how search engines crawl (or read) it.

Google, in particular, has over 200 factors it uses to rank articles on the Web — and those factors may change when their algorithm changes. The SEO audit will help you understand better why some of your content is ranking well, while other content isn’t ranking at all (For anyone who doesn’t know, SEO stands for search engine optimization.)
In this article I'll explain what an SEO audit does, and what you should expect when you get one. Plus, I've listed some free online tools you can use to do some basic website audits of your site.
>>Affiliate notice: Some of the links here may be affiliate links.
Why You Need an SEO audit of your website
One of the best ways to understand how your website is performing on search engines like Google — and how to improve that performance — is to make a detailed analysis of your website in relation to the way that search engines crawl websites.
With this analysis in hand, you can look at how you’ve spent your time and money to optimize your website. Are there changes you need to make, to increase your ROI? and how to spend it in the future.
And that’s where the SEO website audit comes in! On average, an audit of this type can result in a report that’s anywhere from 20 to 30 pages long.
One goal for every website is traffic. Another can be the conversion of visitors into customers. When you improve your website SEO, you increase the chance that search engines like Google will point more readers to your site for answers to their questions.
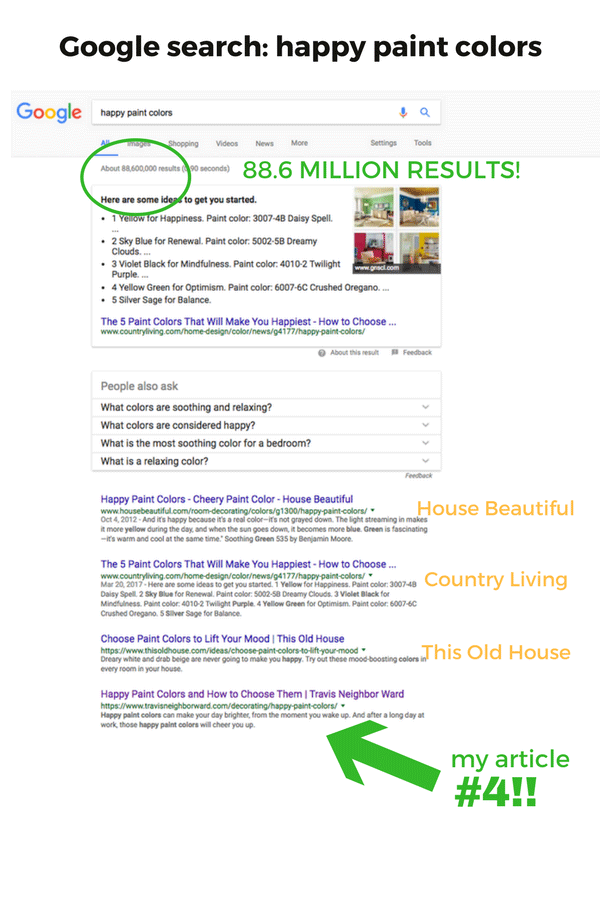
If you're serious about trying to get your web pages to rank on Page 1 of Google searches, you should do SEO audits on a regular basis. I do SEO audits for my website often and use the results to tweak my content and settings.
Whenever my content ranks on Page 1 alongside the biggest editorial websites, I feel so satisfied knowing my hard work paid off! Here's an example from an article I wrote called "Happy Paint Colors and How to Choose Them."
How can you use an SEO audit?
Companies launch websites and blogs to enhance their marketing efforts. In fact, for most companies these online properties form the core of their content marketing plan.
Ideally you have planned your website, and added content, based on a marketing strategy. The website SEO audit will tell you:
- which areas of your site or blog are helping you meet your marketing goals
- which areas can be enhanced
- which areas need to be reduced or eliminated altogether
- where traffic is going on your website
- what your website authority is in the eyes of search engines
- and more.
Content isn’t cheap to produce, and it’s not easy to rank high on Google searches organically (without buying ads). The website SEO audit will show you where you may be hindering your ability to rank high.
With a good SEO audit in hand, you can start planning how to increase your presence on the Web. It will tell you what’s wrong and it will give suggestions about how to improve it.
After you make the improvements, you shouldn’t expect to see results for a few months. It can take search engines anywhere from one to six months to rank a site higher. But sometimes I’ve seen dramatic increases in my rankings in just one month.
It's exciting to track as your page jumps from Page 10 to Page 1. It makes all your SEO efforts worthwhile.
What about online SEO audit tools?
Some companies have created easy tools to give you a quick SEO audit of your site. To use these tools you usually have to give your email address, then the company will send you the report. It’s a great way for them to generate leads for their business.
Good tools like this can be helpful for getting an overview of what you’re up against. But in no way can they give you the complete assessment that you can get when an SEO agency analyzes your site. If you use one of these tools, view it as a starting point.
Also a word of caution: These tools will ask you for a URL to analyze. Keep in mind that some of them analyze only the URL you enter. So if you enter your homepage URL, they’ll only analyze that one page on your website, not the entire site.
An online SEO audit tool that I was introduced to in Fall 2017 is SEOmator.com. They gave me a free subscription so I could test it out, and I have to admit that I was totally impressed by the tool's performance. It gave me a full report on my website after I plugged in my URL, including any issues I had to resolve.
In fact, because of SEOmator's analysis of my website I was able to identify and solve a problem involving a redirect. Up to that point no human I consulted had been able to tell me what was causing the problem. But I was able to solve it on my own with the right information in hand. So that was very cool.
Another online tool you may want to consider trying is Screaming Frog’s SEO Spider. Many SEO pros swear by it. It will crawl your site for free for the first 500 URLs; after that you’ll pay 149£ per year. With Screaming Frog you can do many of the things mentioned in this article. Some of their clients include Disney, Amazon and Google!
To use Screaming Frog, go on their website and download the software to your computer. If you’re not confident about analyzing data on your own, hire an SEO agency to do your audit for you.
Another well-respected SEO audit tools online is SemRush’s website SEO Audit.
There's on-site and off-site SEO auditing
When you look at a website’s SEO health, you need to look at elements that appear on the pages of the site, as well as elements that you can only assess by looking off-site. On-site analysis includes discovering how you’re using your keywords for things like title tags, headlines (H1-H6), and within content.
In both cases you need to use special tools that are able to crawl your site as a search engine bot does, in order to see it from that perspective.
So what elements of a website does the SEO audit look at?
There are many elements that you need to inspect in order to get a complete SEO audit. Here are some of the main ones:
Website speed
The speed of your website is extremely important for user experience (UX) and for search engine bots. Google favors fast sites, so if yours is slow it could negatively affect the ranking of your pages and posts in search results.
Also, readers’ attention span is, on average, about eight seconds. If it takes that long for your website to load, chances are visitors have already decided to search elsewhere.
An SEO audit can tell you exactly what your website speed is and how to improve it. Keep in mind that these improvements are sometimes easy to make by yourself. For instance, you may need to reformat photos and compress them better.
Sometimes you have too many images on a page and you need to eliminate some.
Or you may need to get a faster web hosting company.
But sometimes the improvements will require going into core files of your website and making changes to the code. That’s when you want to hire a programmer to do it if you’re not confident about doing it yourself. You can easily break your website if you mess up.
So regardless, always back up your site before you let anyone make these kinds of changes.
Because speed is so important, if you're using a website theme you need to choose one aimed at fast speed. The first thing I do when I choose a theme is test the speed of its demo sites.
Some developers don’t pay enough attention to this and fill their files with too much code (that's called "code bloat"). You’re going to pay for this later by having a slower site.
No matter what, speeding up your website is definitely worth it when it comes to SEO and website performance.
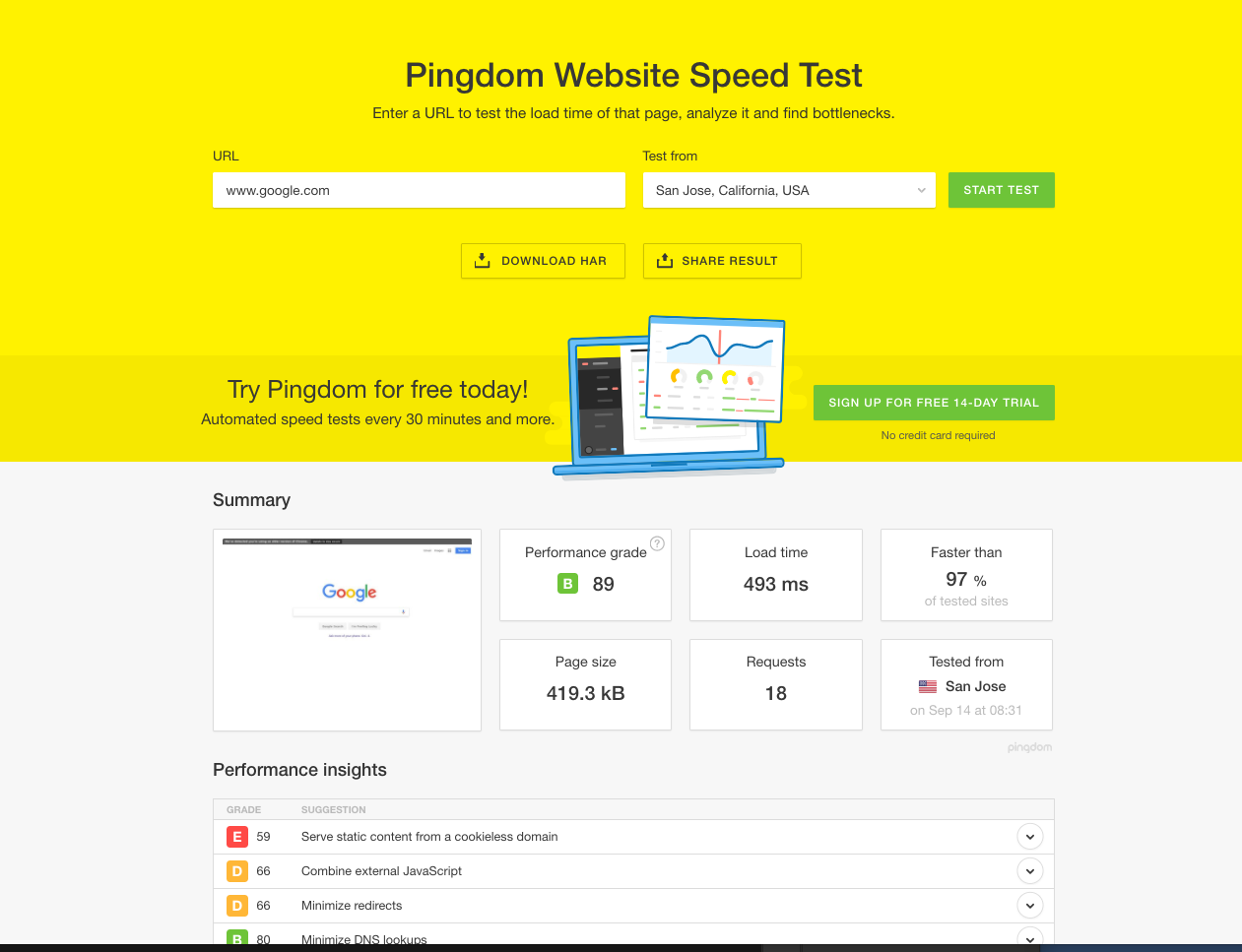
DIY: A quick way to test your website speed is by using Pingdom. But keep in mind that many well-developed websites don't get higher than a score of 90. Here's a speed test I ran on it for Google's home page:
Quality of content
Search engines really pay attention to the quality of your content, from grammar and spelling, to word length and background research you link to. These contribute to the on-page ranking factors. An SEO audit can include an assessment of this.
Targeted keywords
An SEO audit can include a report on whether your site is using keywords that are common in your industry or niche. It can also tell you how much they appear on your site. This is important when it comes to competing with other sites in your area of specialty.
Another thing you want to know is whether you’re using the same targeted keywords for multiple pages on your website. This is called “keyword cannibalism” and it’s something you want to avoid so Google doesn’t penalize your site.
Responsiveness
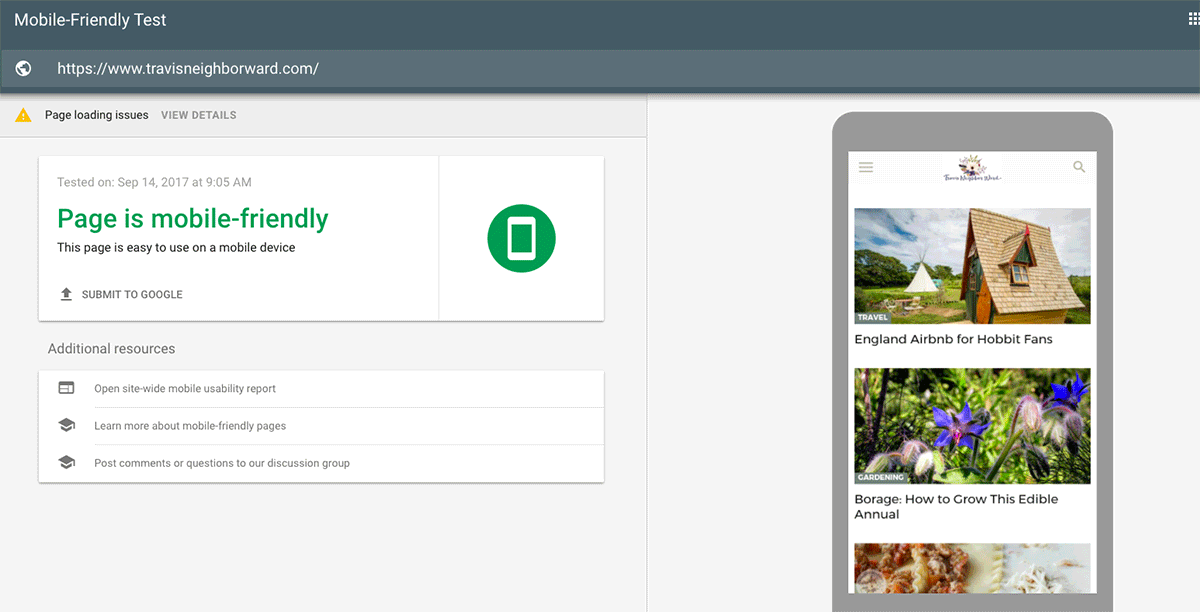
The question here is: How does your website perform on desktop, tablet, and mobile? the pages should automatically resize for each device, unless you have separate websites developed for them.
To see if your website is mobile-friendly, run it through Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
Use of schema
Thanks to an widespread Web project called schema.org, you can assign a specific content type to every piece of content you publish on your website. This "structured data" is really important when it comes to SEO. It tells search engine bots like Googlebot exactly what category the content falls under.
For example, if you write an article you can assign it the “article” schema. If you write a recipe you should give it the “recipe” schema. An item on your online store should have the “product” tag. And so on.
Some themes automatically tag your content with a certain schema (for instance, my Wordpress theme tags everything with “article” because it’s an editorial site). You can always change the schema for individual pieces of content as needed.
Sometimes, if you’re working in Wordpress, you can add a plugin that will inject the schema so you don't need to add it manually.
So a website audit can give you a better understanding of whether your content is being tagged properly with schema vocabulary — or at all.
URL structure
The way you structure your URLs can seriously affect how a search engine (and users) navigate your website. Good URL structure makes it very easy to navigate; poor structure can make it confusing and hard to get around.
URLs should always be under 115 characters long. They should also make it clear what the page is about by using the best keywords within the URL. So this is a poor URL:
website.com/123rwx
This is a good URL:
website.com/washington-travel.
Indexed Pages
When a search engine bot like Googlebot crawls your website, it’s usually not crawling every page. Ideally you have given it a site map (I consider it a necessity for every website), and that tells the bot what’s on your website and where it’s located.
Your site map should leave out anything you don’t want the search engine bots to crawl. If you’re using a Wordpress plugin like Yoast SEO, which I use on all my Wordpress sites, you can specify these details through its settings.
One thing you want to check during your SEO audit is how many pages Google has indexed. You do this using Google Search Console. Then you want to compare that to your total number of pages.
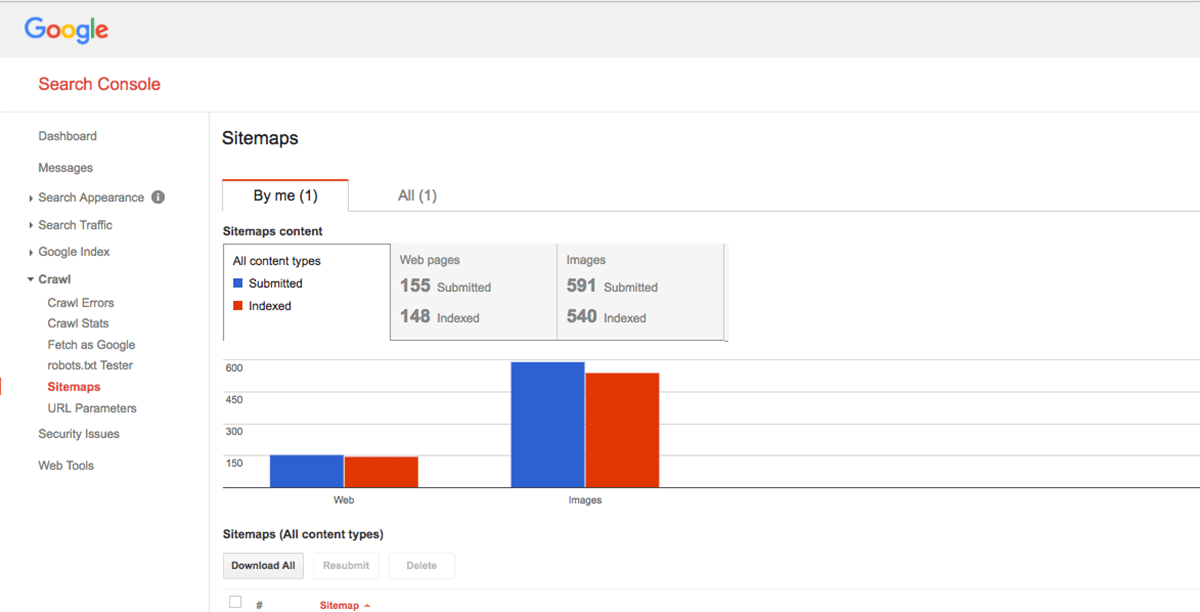
If you see a huge difference, it implies there’s something preventing Googlebot from crawling more of them.
The SEO audit can tell you what those obstacles are.
Duplicate meta descriptions
Every post and page on your website should have a meta description. This is a short description of what is on your web page or post. Most of the time it appears after your title in a search result if you have written it.
If you haven’t written it, search engines will usually pull the first two lines of copy from your post or page.
Search engines like Google don’t like it when the same content appears on different web pages — whether the two copies appear on your website only, or on your website and someone else’s website. It’s called “duplicate content.”
It’s important to make sure that over time you’re not creating duplicate content in your meta descriptions, too.
Duplicate page or post titles
You’d think that you wouldn’t have the same titles on different pages or posts on your website, but it happens. Again, this is frowned upon by search engines. It’s also confusing to readers.
I’ve found that this can sometimes happen as a result of recipe plugins, where you give the recipe a name and then write an associated blog post for it.
So your SEO audit will tell you if you have duplicate titles.
Alt attribute for images
When you add images to your site, you should always give them an alt attribute. This tells search engines what the image is about. It also lets people who can’t see the images know what’s in them.
This alt attribute also contributes to your website’s SEO.
Quality Outlinks
Your pages should link to other websites that are high-quality sites. This may seem counterintuitive (isn’t that giving away link juice to competitors?!), but you need to see it from the search engine’s perspective. By linking to these sites you’re proving that you’ve done your homework. You’re placing your site alongside the others, and Google will see this as a positive thing.
Bad links to your site
You definitely want to disavow links to your site from bad websites — in other words sites that exist for spam purposes.
These sites do things that Google disapproves of. They include things like stuffing keywords into content just to try and rank higher; website cloaking, which is when they show a different version of their website to visitors and search engines; and hidden text, when they show information to search engines that readers can’t see.
You can correct these bad links by going into Google Search Console and telling it not to associate your site with these sites. But first you need to know what they are — and that’s what the SEO audit can tell you. Sometimes it’s hard at first to know which websites linking to yours are legit. It’s yet another reason why you need to manually check each one to be certain.
Broken Links and Error pages
Sometimes you’ll find broken links within your content that lead to pages on other websites that no longer exist.
Or there can be broken links to your own content if you moved it within your website, but haven’t told search engines to redirect the URL for the original pages.
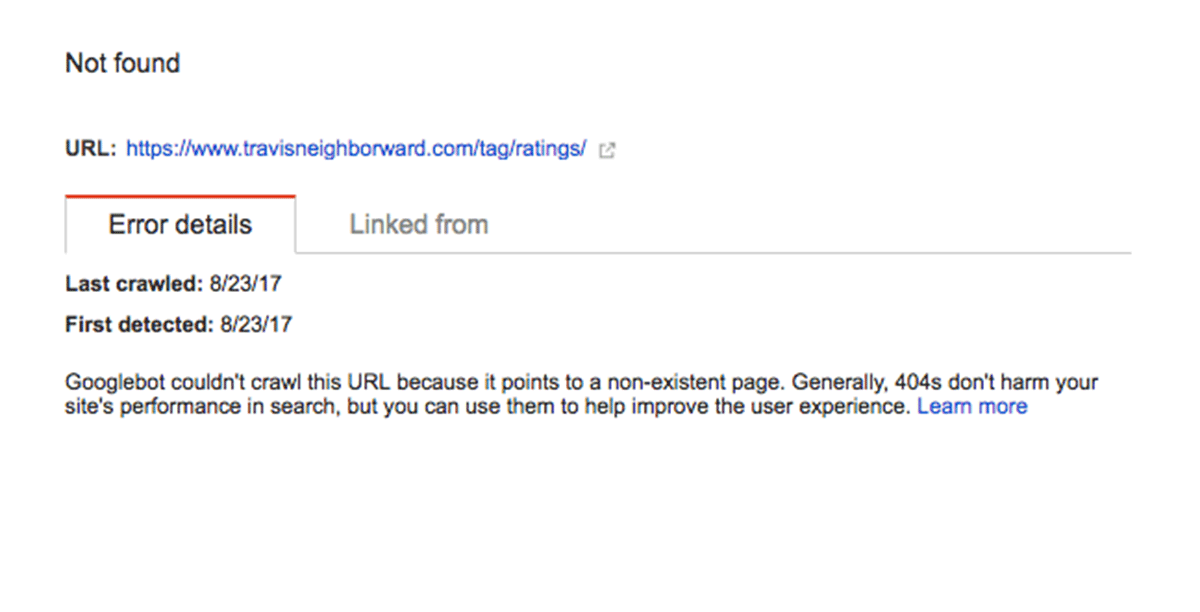
Google files these under “Crawl Errors” in Google Search Console, and divides them into errors found during desktop and smartphone crawls.
For example, let’s say my original post about Italy is here:
https://www.travisneighborward.com/italy.
Then I decide to change that URL to this:
https://www.travisneighborward.com/europe/italy.
If I don’t create what’s called a 301 redirect (that means a permanent redirect), then search engines will only discover the broken link when they try to go to my original URL for the post.
To users this creates a 404 error message (you’ll see something like “404 Oops! This page doesn’t exist!” or something like that).
The real problem for you is that bots can’t crawl URLs with these errors. Chances are they’ll report the error and turn away. That’s obviously bad for your website.
Here’s an example of the details gave me for an error page on my website:
Do you have questions about doing a website audit?
Leave a comment below.


